Potential Difference Voltage Current Emf Explained
It was discovered independently by Joseph Henry in 1832. V I R.

Main Difference Between Voltage And Emf Explained Etechnog
The resistance and the leakage reactance of the windings result in a voltage drop and hence secondary terminal voltage V 2 is the phase difference of E 2 and voltage drop.

. So this phenomenon of generating induced emf or current because of changing flux is called the Electromagnetic Induction. Access the answers to hundreds of Electric current questions that are explained in. V 2 E 2.
Terminal Voltage emf. In Faradays first experimental demonstration August 29 1831 he wrapped two wires around opposite sides of an iron ring or torus an arrangement similar to a modern toroidal transformercitation needed Based on his. Ohms law states that Voltage Current x Resistance which is how we calculate the number of watts given a.
The flow of electricity caused by the electrical pressure of the voltage is called current and is measured in Amperes Amps. The electromotive force created will explain the Seebeck effect and the equation of electromotive force in terms of the Seebeck coefficient is given by. An AC power supply puts out a voltage as.
If you move the rod through the field however an emf is induced between the ends of the rod causing current to flow. If a current I should flow through a resistor R the voltage V can be calculated. Enter the email address you signed up with and well email you a reset link.
Due to this flux an emf is induced in the coil. Ohms Law can be rewritten in three ways for calculating current resistance and voltage. Voltage can be compared to the pressure of water stored in large pipe refer above analogy.
Ampere can be compared to the rate or speed at which water flows through each of the smaller pipes. Unit of measure of electric potential difference or voltage. I can be calculated.
20 as a heuristic method although the underlying theory is reasonably accessible 21It depends on the recording of the current noise only. The signal is filtered with a high-pass filter with a cut-off. Emf An emf electromotive force is the potential difference developed or that emanate from the source of electrical energy say battery which is capable of driving an electric current in a circuit.
σ - The local conductivity. When changing current is passed through a closed coil varying magnetic flux develops in it. Therefore current I 2 is drawn lagging E 2 by an angle ϕ 2.
What are the potential difference and current. The higher voltage that is applied to a given load the higher the Amps that will flow through it will be. Current I 0 lags the voltage V 1 by 90 degrees.
RESISTANCE LOAD Resistance is what limits the current flow for a given voltage. In the above DC motor controller design the pot adjustment creates a varying potential difference across the gate of the mosfet and. A Terminal voltage is less than the emf.
First Version of the voltage formula. Voltage potential difference between two points VIR potential energy per unit charge. If you have a fixed voltage.
Electromagnetic induction was discovered by Michael Faraday published in 1831. Cottis in Techniques for Corrosion Monitoring Second Edition 2021 54310 Coulomb counting. Akinremi 11-21-2015 0436 AM really awesome Thnx for remembering to me my college time and it is really awesome.
These moving charges are deflected by the field toward one end of the rod creating a potential difference. Is equal to the terminal voltage when no current is drawn. This induced emf generates an induced current in it.
This is because when you move the metal rod through the field you are moving all the electrons in the rod. W refers to watts which is a combination of voltage and current. When the electric cell is in a closed circuit the current flows through the circuit.
There is a fall of potential across the internal resistance of the cell. The power factor of the load is lagging. Electrical Electronics Technology Engineering Education Circuit Diagram Connection wiring block diagram.
Unit of measure of electric current through a conductor. If there is a voltage V across a resistor R a current I flows through it. The local current density can be calculated using the formula Where ΔV - The potential difference developed E_emf - Electromotive force.
As can be seen the mosfet is rigged as a source follower or a common drain mode to learn more about this configuration you may refer to this post which discusses a BJT version nevertheless the working principle remains the same. The coulomb counting or CoulCount method was developed by Schmitt et al.
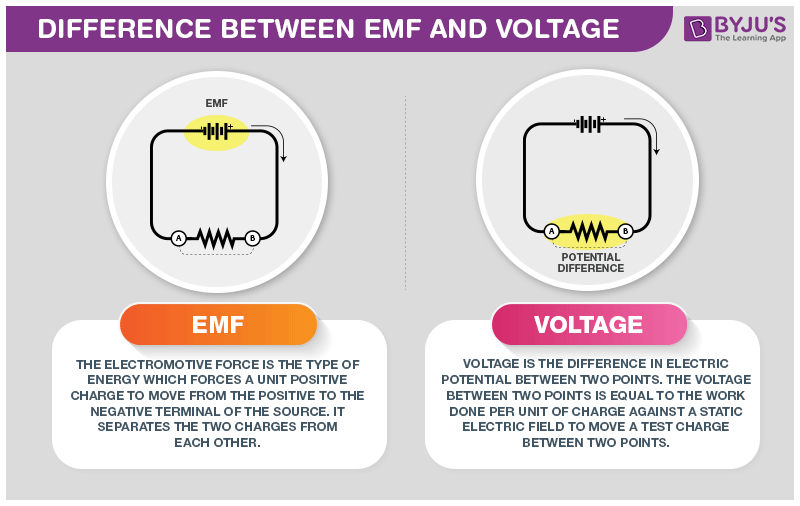
Difference Between Emf And Voltage With Its Practical Applications In Real Life

Voltage Vs Emf Difference Between Potential Difference Emf Basic Electronics Niket Shah Youtube
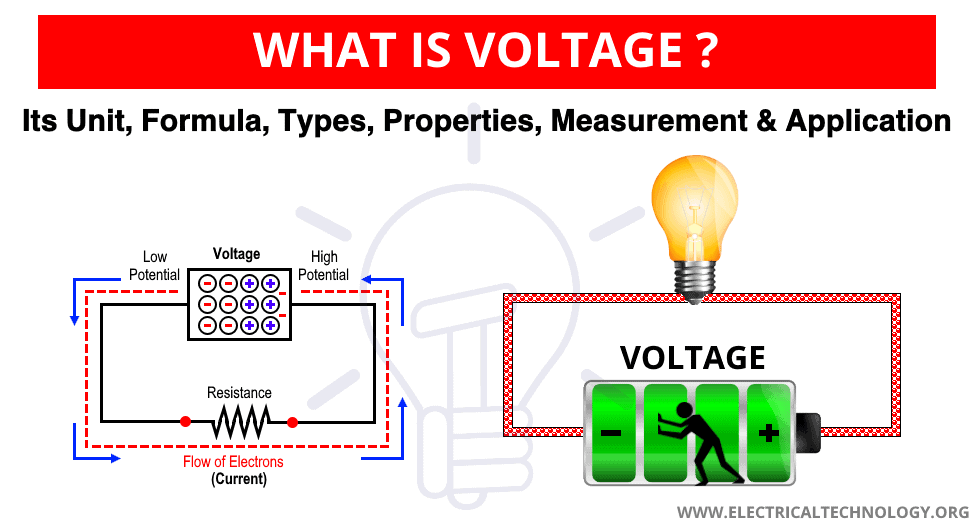

Comments
Post a Comment